What is a Smart Contract
Smart contract are poised to revolutionize how we conduct transactions and agreements across various industries.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, smart contract have emerged as one of the most transformative and promising innovations. These self-executing contracts, with the ability to automate and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries, are changing the way we conduct transactions, from simple agreements to complex financial instruments. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of smart contracts, exploring their definition, functionality, applications, and the potential they hold for revolutionizing various industries.
Blockchain technology, which gained notoriety as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has evolved far beyond digital currencies. At the forefront of this evolution are smart contracts, offering a powerful means of automating and securing agreements in a decentralized and tamper-resistant manner. This guide aims to demystify smart contracts, shedding light on their definition, functionality, use cases, and the transformative potential they hold.
What is a Smart Contract?
The Birth of Smart Contracts
The concept of smart contracts was first introduced by computer scientist and legal scholar Nick Szabo in the early 1990s. Szabo envisioned self-executing contracts with the terms and conditions directly written into code. However, it was not until the emergence of blockchain technology that the practical implementation of smart contracts became possible.
The Definition of a Smart Contract
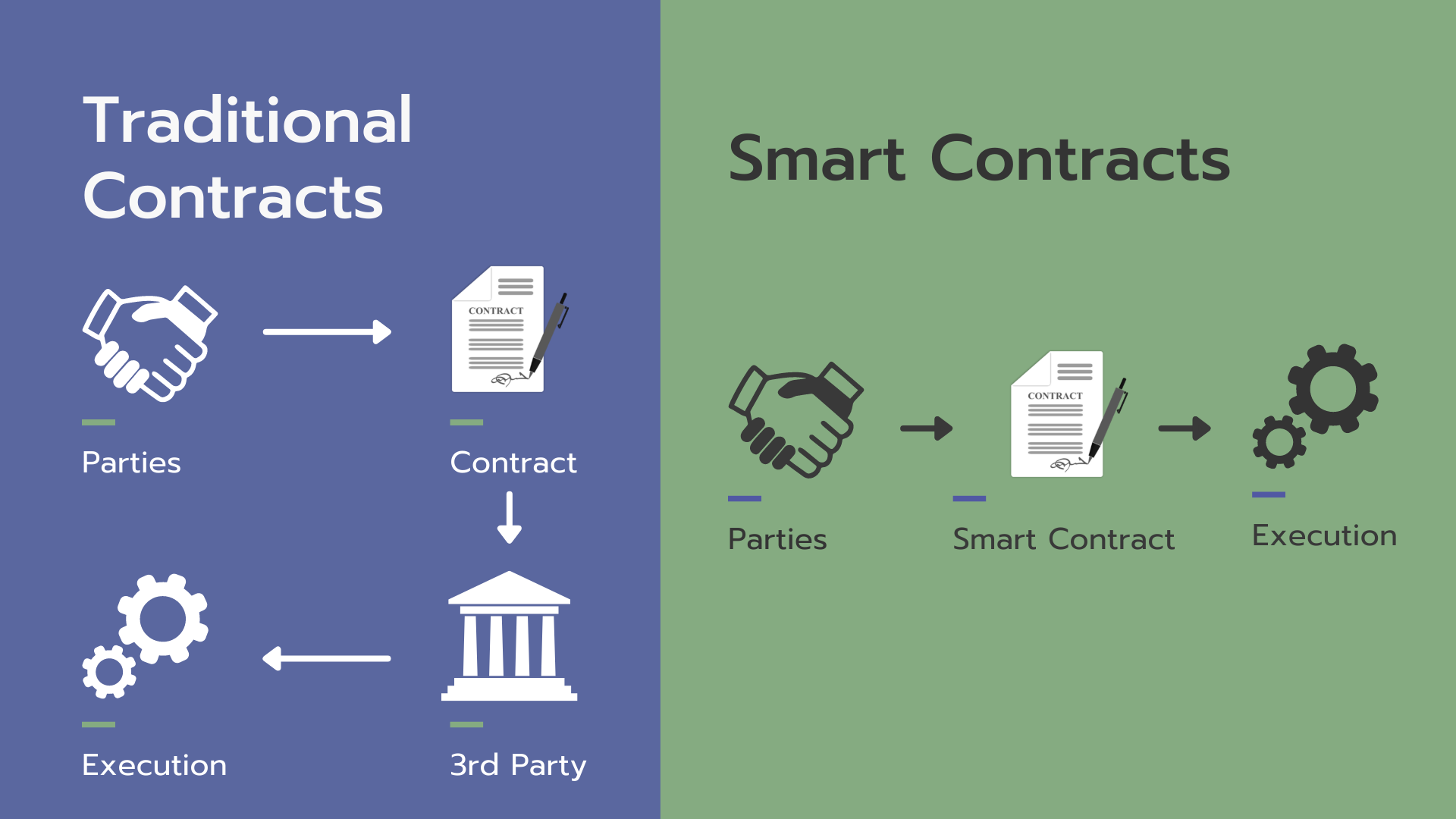
A smart contract is a self-executing and self-enforcing agreement with the terms and conditions of the contract written directly into code. These contracts run on a blockchain and automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing transparency and security.
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts operate on the principles of blockchain technology. Here's a simplified overview of their functionality:
- Agreement Creation: The parties involved in a transaction agree to the terms and conditions of the smart contract.
- Coding the Contract: A developer writes the contract's code, specifying the rules and conditions that trigger execution.
- Deployment: The smart contract code is deployed to a blockchain, making it immutable and accessible to all relevant parties.
- Triggering Conditions: The contract waits for predefined conditions (e.g., payment received, shipment confirmed) to be met.
- Self-Execution: When the conditions are met, the contract automatically executes the agreed-upon actions, such as releasing funds or transferring ownership.
Key Components of a Smart Contract
Self-executing Code
The heart of a smart contract is its code, which defines the rules, conditions, and actions to be executed. This code is tamper-resistant and transparent, ensuring that the contract operates as intended.
Decentralized Ledger
Smart contracts run on a blockchain, which serves as a decentralized ledger. This ledger records all transactions and contract executions, providing transparency and immutability.
Digital Signature
Each party involved in a smart contract signs the agreement with a digital signature, confirming their commitment to the contract's terms. These signatures are cryptographically secure and traceable.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Trust and Transparency
Smart contracts are transparent, and their execution is verifiable on the blockchain, reducing the need for trust in intermediaries.
Efficiency and Automation
Automation of contract execution reduces the time and costs associated with traditional agreements and eliminates the potential for human error.
Security and Immutability
Smart contracts are highly secure, thanks to blockchain technology. Once deployed, they are immutable and resistant to tampering.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have found applications in various industries:
Financial Services
Smart contracts are used for lending, insurance, and automated trading, among other financial services.
Supply Chain Management
They enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud and errors.
Real Estate
Smart contracts simplify property transactions, automating tasks like title transfers and escrow.
Healthcare
They enable secure and efficient sharing of patient data and automate insurance claims processing.
Legal Industry
Smart contracts streamline legal agreements and reduce the need for legal intermediaries.
Challenges and Limitations
Smart contracts face challenges, including:
Legal Recognition
Their legal status varies by jurisdiction, and enforcing them in traditional legal systems can be complex.
Complex Coding
Writing error-free code is crucial; otherwise, vulnerabilities can be exploited.
Scalability
Blockchain networks must address scalability issues to handle a growing number of smart contracts.
Smart Contract Platforms
Several blockchain platforms support the creation and execution of smart contracts:
Ethereum
Ethereum is a pioneer in smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Binance Smart Chain
Binance Smart Chain offers compatibility with Ethereum and lower transaction fees.
Cardano
Cardano aims to provide secure and scalable smart contracts.
Polkadot
Polkadot offers interoperability between different blockchains and smart contract support.
Future Trends and Developments
The future of smart contracts holds exciting possibilities, including improved scalability, wider adoption, and enhanced integration with emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT).
Smart contracts are poised to revolutionize how we conduct transactions and agreements across various industries. Their ability to automate, secure, and reduce the need for intermediaries positions them as a cornerstone of the blockchain revolution. As the technology continues to evolve and gain broader acceptance, smart contracts are set to play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of decentralized transactions and digital trust.
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg)
